Common Procedures
Common Procedures
Common Procedures
For answers to questions about the services we offer and to schedule an appointment, please call our dental office!
 Write your caption hereButton
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
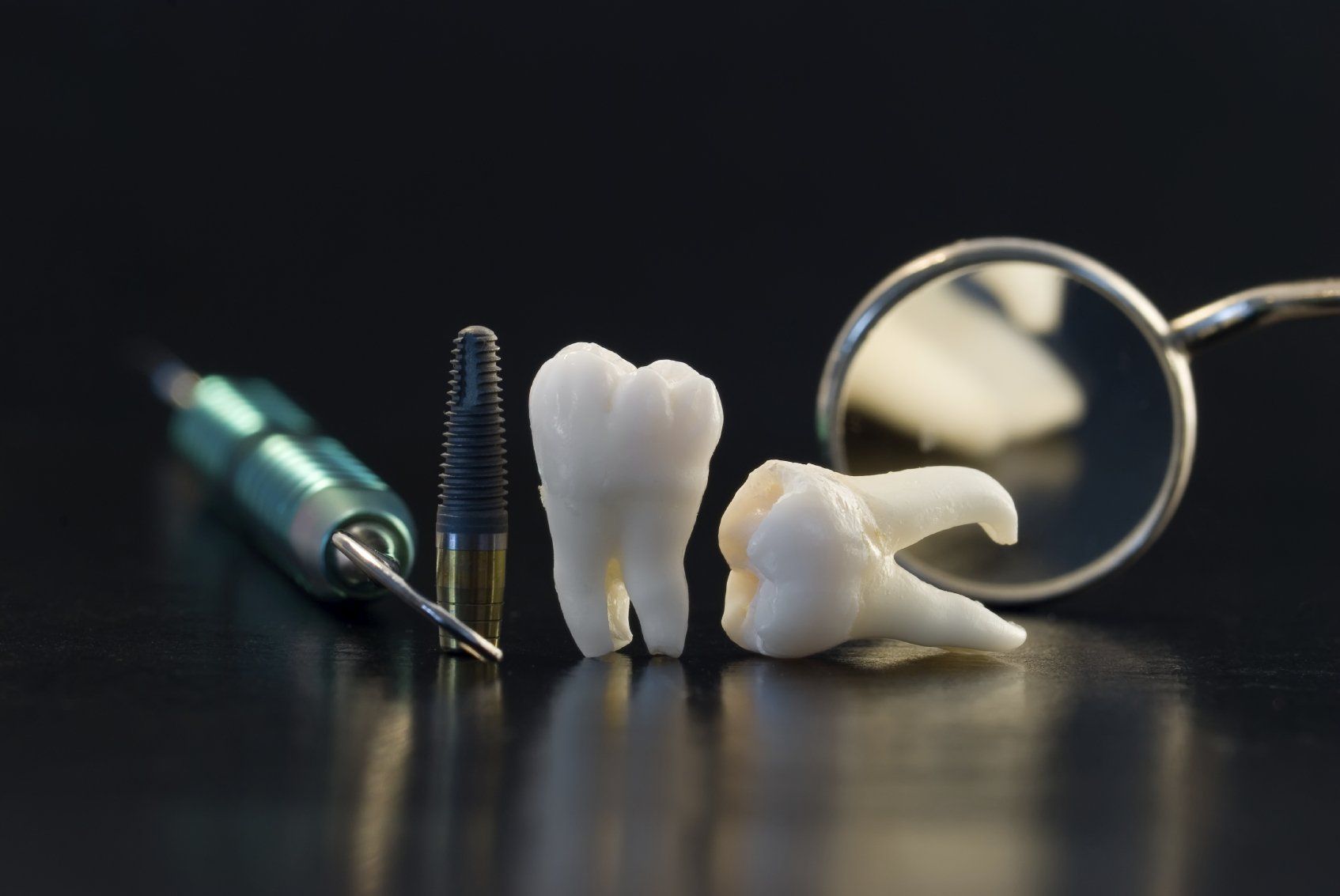
Crowns & Bridges
Crowns area restorative procedure used to improve your tooth's shape or to strengthen a tooth. Crowns are most often used for teeth that are broken, worn or have portions destroyed by tooth decay. A crown is a "cap" cemented onto an existing tooth that usually covers the portion of your tooth above the gum line. In effect, the crown becomes your tooth's new outer surface. Crown's can be made of porcelain, metal or both. Porcelain crowns are most often preferred because they mimic the translucency of natural teeth and are very strong.
A bridge may be used to replace missing teeth, help maintain the shape of your face and alleviate stress on your bite. A bridge replaces missing teeth with artificial teeth, looks great and literally bridges the gap where one or more teeth may have been. Your bridge can be made from gold, alloys, porcelain or a combination of these materials and is bonded onto surrounding teeth for support. The success of any bridge depends on its foundation-the other teeth, gums or bone to which it is attached. Therefore, it is very important to keep your existing teeth, gums and jaw healthy and strong.
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton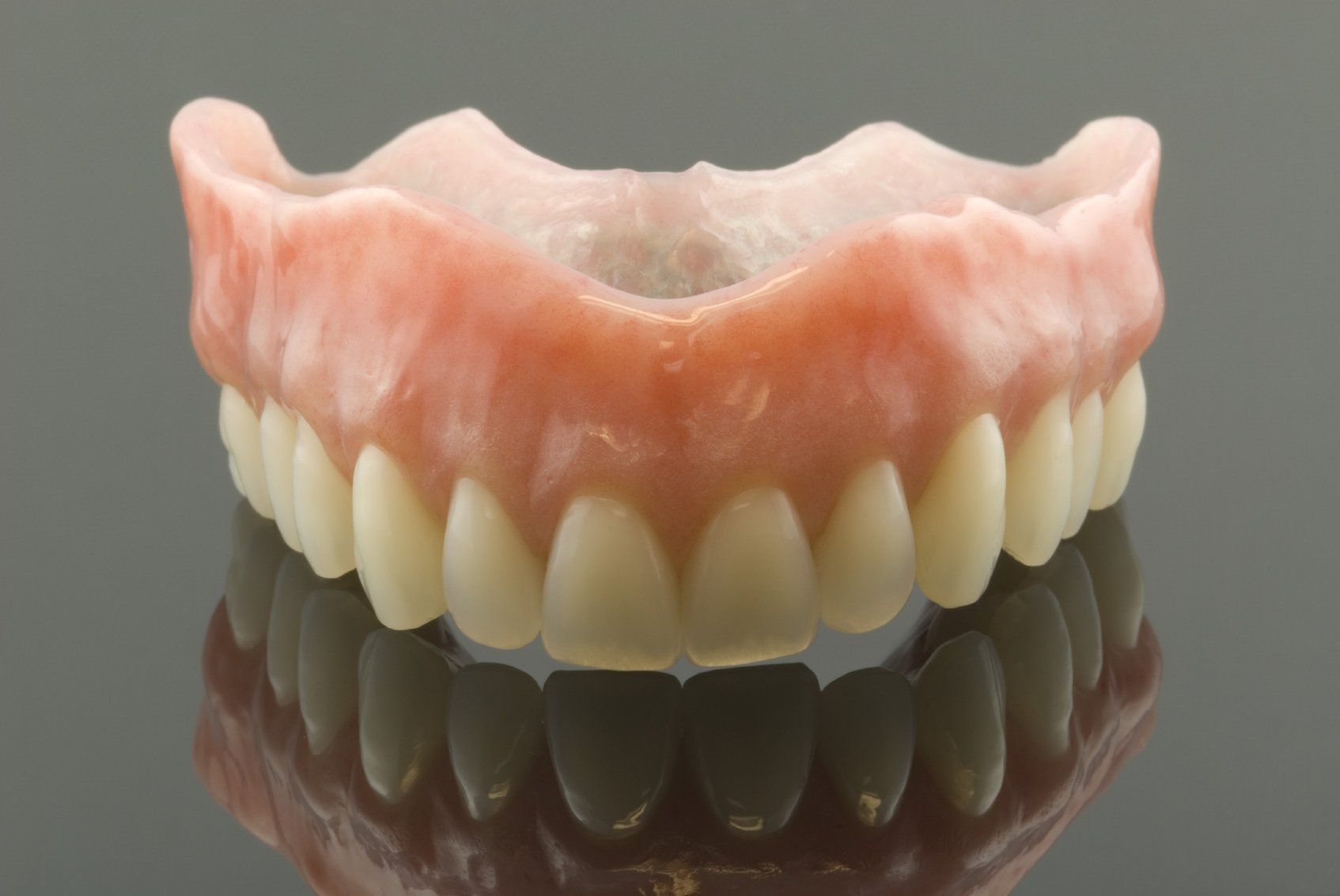
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
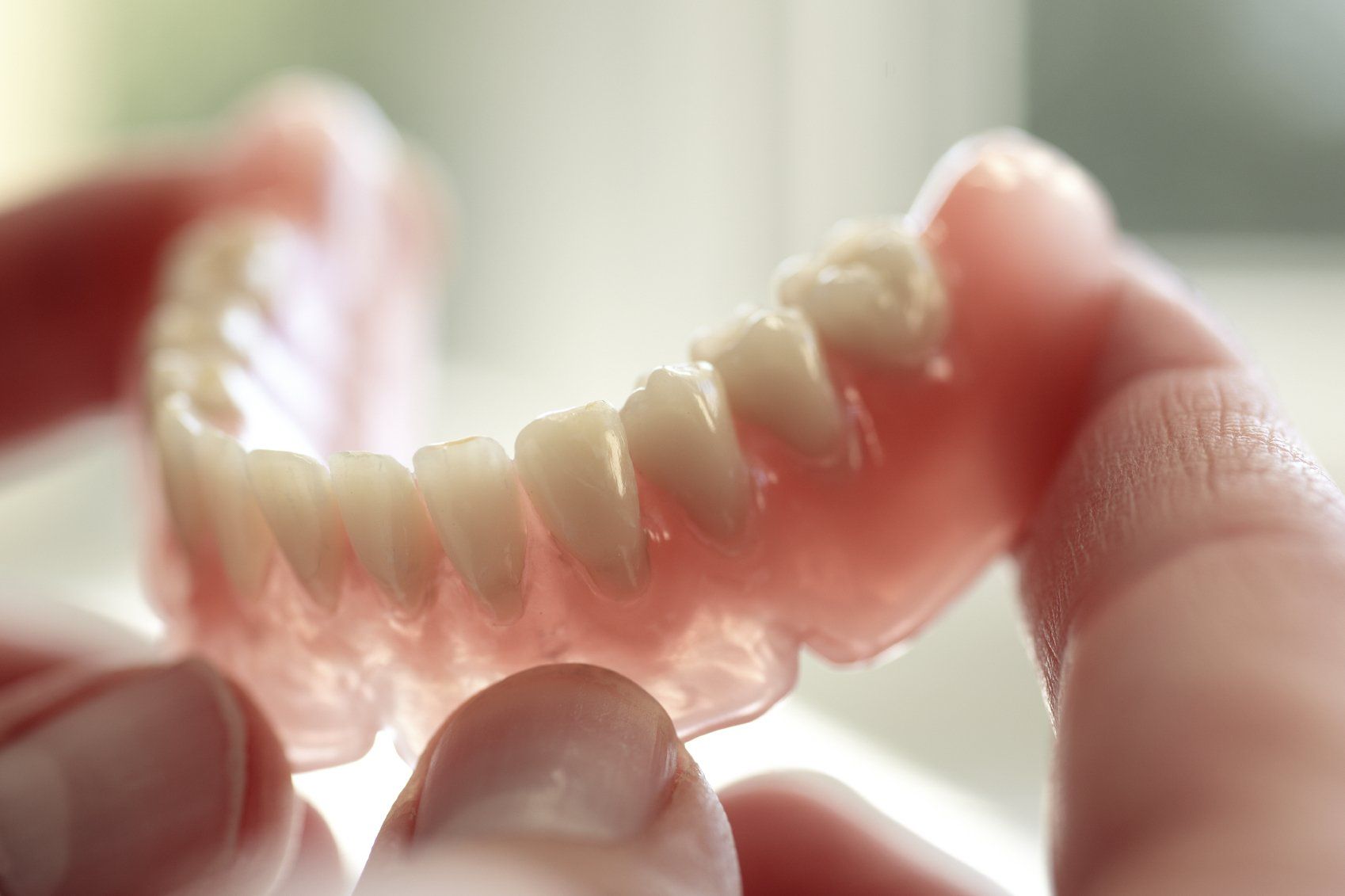
Dentures & Partials
Dentures are a natural-looking, removabl e replacement for teeth. There are two types of dentures: full denture and partial denture. Full dentures are for patients who have had all their natural teeth removed. A partial denture is used to fill in gaps where a few permanent teeth have been removed. It attaches to a metal frame that connects or hooks onto your natural teeth. Just like your natural teeth, dentures need to be properly cleaned and cared for. Use a gentle cleanser to brush your dentures, always keep them moist when they are not being worn and be sure to keep your tongue and gums clean as well.
Root Canal
When a tooth is cracked or has deep decay, bacteria can enter the pulp tissue and germs can cause an infection inside the tooth. If left untreated, an abscess may form. A root canal treatment can save your tooth and get you out of pain. In one to three visits, a root canal involves the dentist removing the infected tissue. The interior of the tooth is then cleaned and sealed. Last, the tooth is filled with composite material. If your tooth has extensive decay, your dentist may suggest placing a crown to strengthen and protect the tooth from breaking.

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Extractions
There are times when it is necessary to remove a tooth. Sometimes, a baby tooth has long roots that prevent it from falling out naturally and it must be extracted to make room for the permanent tooth to erupt. Other times, a tooth may have so much decay that it puts the surrounding teeth at risk of decay, so your dentist may recommend removal and replacement with a bridge or implant. Infection, orthodontic correction or problems with a wisdom tooth can also require an extraction of a tooth.
The root of each tooth is encased within your jawbone in a "tooth socket," and your tooth is held in that socket by a ligament. In order to extract a tooth, your dentist must expand the socket and separate the tooth from the ligament holding it in place. While this procedure is typically very quick, it is important to share with your doctor any concerns or preferences for sedation.
Once a tooth has been removed, neighboring teeth may shift, causing problems with chewing or with your jaw joint function. To avoid these complications, your dentist may recommend that you replace the extracted tooth.
Sealants
Sometimes brushing is not enough, especially when it comes to those hard-to-reach spots in your mouth. It is difficult for your toothbrush to get in-between the small cracks and grooves on your teeth. If left alone, those tiny areas can develop tooth decay. Sealants give your teeth extra protection against decay and help prevent cavities.
Nightguards
If you often wake up with jaw pain, earaches, headaches or if you find yourself clenching or grinding your teeth, you may have a common condition called "bruxism". Many people do not even know that they grind their teeth, as it often occurs when you are sleeping. If not corrected, bruxism can lead to broken teeth, cracked teeth or even tooth loss.
There is an easy, non-invasive treatment for bruxisml nightguards. Nightguards are an easy way to prevent the wear and damage that teeth-grinding causes over time. Custom-made by your dentist from soft material to fit your teeth, a nightguard is inserted over your top or bottom arch and prevents contact with the opposing teeth.
Wisdom Teeth
Wisdom teeth are types of molars found in the back of your mouth. They usually appear in the late teens or early twenties, but may become impacted (fail to erupt) due to lack of room in the jaw or angle of entry. When a wisdom tooth is impacted, it may need to be removed. If not, you may develop gum tenderness, swelling, or even severe pain. Impacted wisdom teeth that are partially or fully erupted tend to be quite difficult to clean and are susceptible to tooth decay, recurring infections and even gum disease.
Wisdom teeth are typically removed in the late teens or early twenties because there is a greater chance that the teeth's roots have not fully formed and the bone surrounding the teeth is less dense. These two factors can make extraction easier as well as shorten the recovery time.
Sedation Dentistry
Do you have fear or anxiety of being at the dentist? Do you have a hard time sitting still for long periods of time? Do you have difficult time getting (and staying) numb from anesthetics? Sedation dentistry may be the solution! We are pleased to offer our patients the option of comfortable, safe and effective sedation. There are several benefits of sedation dentistry, including: No memory of undergoing the procedure, no sense of time while under sedation, no sense of smell or sound and no fear or anxiety during treatment.
There is no need to nervous about sedation dentistry. It is closely regulated by law. We are licensed to perform sedation dentistry in our office by the American Dental Association and you will find that we are both respectful and professional at all times. Call our office to learn more about the types of sedation dentistry we offer.